Key Stats
Market Capitalization: $190.22 billion (as of November 2025)
Annual Revenue: $94.53 billion (trailing twelve months)
Total Employees: Over 200,000 worldwide
Stock Symbol: NYSE: DIS
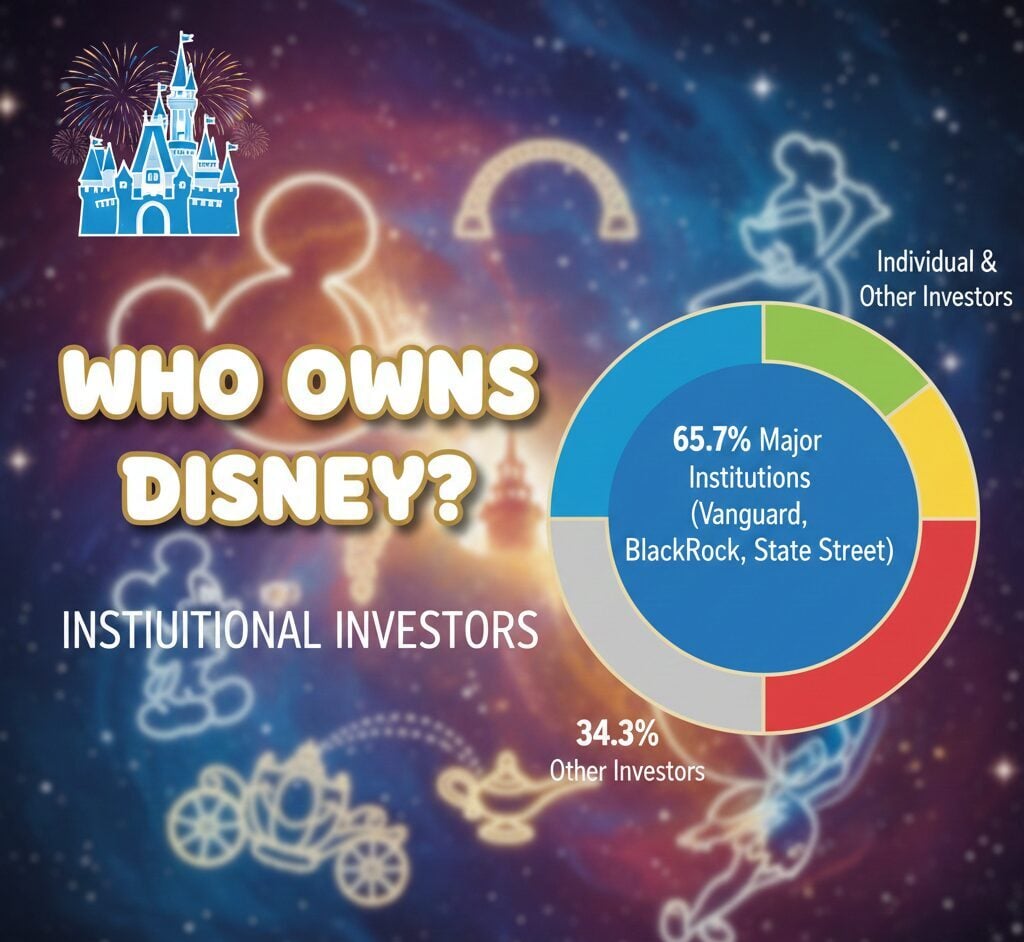
The Walt Disney Company stands as one of the entertainment industry’s most recognizable brands. Institutional investors own approximately 65.7 percent of Disney shares, with major asset management firms like Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and State Street controlling the largest stakes.
The entertainment giant operates through three primary business segments including Disney Entertainment, ESPN, and Disney Experiences. Recent corporate developments include the resumed dividend payments in December 2024 and the appointment of James Gorman as Board Chairman in January 2025. The company continues expanding its global presence through new theme park projects in Asia and the Middle East while strengthening its streaming platforms Disney+ and Hulu.
ABC television network ownership flows through Disney’s Entertainment division, which the company acquired in 1996 for $19 billion. Disney’s portfolio extends beyond broadcasting to include film studios like Pixar, Marvel Studios, and Lucasfilm, positioning it among the top entertainment conglomerates alongside Time Warner and Universal Studios.
Who owns Disney?
Institutional investors dominate Disney’s ownership structure through their collective control of roughly 65.7 percent of outstanding shares. This concentration gives major financial institutions considerable influence over corporate governance decisions, board appointments, and strategic direction.
Institutional Control Structure
The absence of significant founder or family ownership means control operates through board-shareholder dynamics rather than concentrated individual stakes. This structure allows institutional investors to exert pressure on management regarding cost reductions, business reorganizations, and strategic acquisitions.
Shareholder Influence on Governance
The 2024 proxy fight illustrated this dynamic when Nelson Peltz’s Trian Fund Management attempted to secure board representation to implement corporate changes. Shareholders ultimately voted to retain the existing board, demonstrating how distributed ownership influences major governance decisions.
Individual investors and insiders account for approximately 34.3 percent of Disney shares. These shareholders include board members, senior executives, and retail investors. While their collective stake represents minority ownership, individual shareholders can influence outcomes through proxy votes during shareholder meetings.
History of Disney Co-founders
Brothers Walt Disney and Roy Oliver Disney established the Disney Brothers Cartoon Studio on October 16, 1923, in Hollywood, California. The founding date marks when distributor Margaret Winkler contracted to distribute the Alice Comedies, a series combining live-action footage with animation.
Walt Disney’s Creative Vision
Walter Elias Disney was born in Chicago in 1901 and developed animation skills while working for the Kansas City Film Ad Company. After his first venture, Laugh-O-Gram Studio, declared bankruptcy in 1923, Walt relocated to Los Angeles with his unfinished film Alice’s Wonderland. His brother Roy was recovering from tuberculosis in California when Walt proposed starting their animation business together.
Walt handled the creative aspects of the studio, designing characters and directing animated productions. He created Mickey Mouse in 1928 after losing rights to his previous character, Oswald the Lucky Rabbit. This experience taught Walt to maintain ownership of intellectual property, a principle that shaped Disney’s business practices for decades.
Roy Disney’s Business Leadership
Roy Oliver Disney, born in 1893, managed the company’s financial operations and business strategy. He served as Disney’s first chief executive officer starting in 1929 and shared the chairman role with Walt from 1945 onward. Roy’s financial acumen enabled the studio to survive difficult periods and fund ambitious projects.
Following Walt’s death in 1966, Roy postponed retirement to oversee construction of Walt Disney World. He insisted the Florida resort bear his brother’s name to honor Walt’s legacy. Roy passed away in December 1971, just months after Walt Disney World opened. The company’s survival and growth through the 1970s reflected the strong foundation both brothers established.
Who is on the board of directors for Disney?
Disney’s Board of Directors consists of ten members who guide strategic direction and corporate governance. James Gorman serves as Board Chairman effective January 2025, succeeding Mark Parker who departed after nine years of service. The board maintains diverse expertise across finance, technology, operations, and entertainment sectors.
Leadership and Executive Direction
Robert Iger holds dual roles as Chief Executive Officer and board member. His leadership tenure includes transformative acquisitions such as the $71.3 billion purchase of 21st Century Fox in 2019. Iger previously served as CEO from 2005 to 2020 before returning to the position in 2022.
James Gorman chairs the Succession Planning Committee, working to identify Disney’s next chief executive officer. The company expects to announce Iger’s successor in early 2026. Gorman brings extensive financial services experience from his tenure as Morgan Stanley’s CEO from 2010 to 2023.
Finance and Technology Expertise
Mary Barra serves on the board while maintaining her position as Chair and CEO of General Motors. Her automotive industry experience provides insights on manufacturing, supply chain management, and consumer products. Barra joined Disney’s board to contribute operational expertise from leading a global corporation.
Amy Chang brings technology sector knowledge from executive positions at Cisco Systems and Google. She currently serves on Procter & Gamble’s board, contributing consumer products experience. Her digital transformation expertise aligns with Disney’s streaming strategy expansion.
International Business Operations
Jeremy Darroch previously served as Group Chief Executive of Sky, bringing international media and broadcasting experience. His expertise in subscription-based television operations provides valuable perspective on Disney’s streaming business model across European markets.
Michael Froman currently serves as President of the Council on Foreign Relations and previously held positions as Vice Chairman at Mastercard. His international business relationships and trade policy knowledge support Disney’s global expansion strategy.
Consumer Brand Management
Carolyn Everson held senior roles at Instacart, Meta Platforms, and Microsoft, developing expertise in advertising and marketing partnerships. She serves on boards for Coca-Cola and Under Armour, contributing consumer brand insights. Her digital advertising experience supports Disney’s ad-supported streaming initiatives.
Calvin McDonald serves as CEO of lululemon athletica, bringing retail and consumer brand management experience. His leadership of a lifestyle brand provides perspectives on customer engagement and brand positioning relevant to Disney’s consumer products division.
Financial Planning and Advisory
Maria Elena Lagomasino leads WE Family Offices as CEO and Managing Partner after senior executive positions at JP Morgan Private Bank and Chase Manhattan Bank. Her wealth management expertise supports board oversight of Disney’s financial strategy and capital allocation decisions.
Derica Rice brings pharmaceutical and healthcare industry experience from executive positions at CVS Health and Eli Lilly. His financial planning background and operational leadership contribute to board discussions on Disney’s business unit performance and strategic investments.
Largest shareholders of Disney
Disney Institutional Ownership Distribution
Sources: Disney Investor Relations, MacroTrends Disney Market Cap Data
Disney’s ownership structure mirrors other major entertainment companies like Paramount Global and CBS Corporation, where institutional investors hold controlling stakes. The concentration of shares among major asset managers reflects broader trends in corporate America, where index funds and passive investment strategies have grown substantially over the past two decades.
This ownership pattern contrasts with family-controlled media companies or founder-led technology firms. Instead, Disney operates under a governance model where dispersed institutional ownership creates checks and balances through shareholder voting and board oversight. The structure has enabled the company to pursue long-term strategic initiatives while maintaining accountability to a broad base of investors.
Disney’s competitive position in streaming, theme parks, and content production continues attracting institutional investment despite challenges facing traditional media companies. The company’s diversified revenue streams across multiple business segments provide stability compared to pure-play streaming services or traditional broadcast networks. As the entertainment landscape evolves, Disney’s ownership structure positions it to adapt through strategic investments guided by board oversight and shareholder input.
Three major asset management firms control the largest institutional stakes in Disney, collectively holding over 18 percent of outstanding shares. These firms manage investments on behalf of pension funds, mutual funds, and individual retirement accounts, giving them substantial voting power in corporate decisions.
Vanguard Group Holdings
Vanguard Group maintains the largest institutional position with approximately 8.71 percent of Disney shares, representing roughly 155.86 million shares. The Pennsylvania-based investment management firm operates as one of the world’s three largest asset managers. Vanguard’s Disney stake primarily consists of holdings in index funds and exchange-traded funds that track major market indices.
The firm’s passive investment strategy means it typically votes proxies in alignment with management recommendations while maintaining engagement on governance issues. Vanguard’s massive Disney position gives it significant influence during shareholder votes on director elections, executive compensation, and major corporate transactions.
BlackRock Investment Position
BlackRock holds approximately 7.32 percent of Disney shares, totaling around 131.54 million shares. Based in New York City, BlackRock manages assets for institutional clients, governments, and individual investors across global markets. The firm’s Disney holdings span multiple investment products including iShares ETFs and actively managed funds.
BlackRock maintains dedicated teams for corporate governance engagement and proxy voting. The firm regularly communicates with Disney management on strategic initiatives, sustainability practices, and financial performance. Its substantial stake ensures BlackRock’s voice carries weight in shareholder deliberations.
State Street Corporation Stake
State Street Corporation owns approximately 4.39 percent of Disney shares, representing around 79.02 million shares. The Boston-based financial services company completes the “Big Three” asset managers alongside Vanguard and BlackRock. State Street’s holdings primarily consist of positions in SPDR ETFs and institutional investment mandates.
The firm actively engages with portfolio companies on environmental, social, and governance issues. State Street’s proxy voting guidelines emphasize board diversity, executive compensation alignment, and shareholder rights. Its significant Disney position enables meaningful influence on corporate governance matters.
Morgan Stanley Position
Morgan Stanley holds roughly 2.5 percent of Disney shares, totaling approximately 47 million shares. The investment bank provides wealth management and institutional securities services alongside traditional banking operations. Morgan Stanley’s Disney holdings reflect both proprietary positions and client asset management.
The firm maintains research coverage of media and entertainment sectors, publishing regular analysis of Disney’s financial performance and strategic initiatives. Similar to Warner Bros and other major studios, Disney receives close scrutiny from Wall Street analysts tracking entertainment industry trends.
Geode Capital Management
Geode Capital Management owns around 2 percent of Disney shares, representing approximately 35 million shares. The Boston-based asset manager focuses on quantitative investment strategies and index fund management. Geode operates as a subsidiary of Fidelity Investments while maintaining independent investment operations.
The firm’s Disney holdings primarily consist of index fund positions tracking broad market benchmarks. Geode’s systematic investment approach emphasizes diversification across sectors including media, entertainment, and consumer discretionary stocks.
Individual Shareholder Stakes
Robert Iger owns approximately 226,770 Disney shares, representing roughly 0.01 percent of the company. His holdings reflect accumulated equity compensation and direct purchases during his tenure. Other significant individual shareholders include board members and senior executives with smaller percentage stakes.
Brent Woodford, Executive Vice President of Controllership, holds about 38,000 shares. Board members Maria Elena Lagomasino, Mark Parker, and Mary Barra each own positions ranging from 19,000 to 28,000 shares. These individual stakes align executive and director interests with broader shareholder value creation.
FAQs
What percentage of Disney does Vanguard own?
Vanguard Group owns approximately 8.71 percent of Disney shares, making it the largest institutional shareholder with around 155.86 million shares held through various index funds and ETFs.
Is Disney still owned by the Disney family?
No Disney family members hold significant ownership stakes in the company. Institutional investors own roughly 65.7 percent of shares, with individual investors and insiders controlling approximately 34.3 percent.
Who is the current CEO of Disney?
Robert Iger serves as Disney’s Chief Executive Officer. He returned to the role in 2022 after previously leading the company from 2005 to 2020. Disney plans to announce his successor in early 2026.
How many Disney shares are outstanding?
Disney has approximately 1.8 billion outstanding shares as of November 2025. The company trades on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol DIS with a market capitalization exceeding $190 billion.
When was Disney founded?
Walt Disney and Roy Disney founded Disney Brothers Cartoon Studio on October 16, 1923, in Hollywood, California. The company celebrated its 100th anniversary in 2023, marking a century of entertainment innovation.