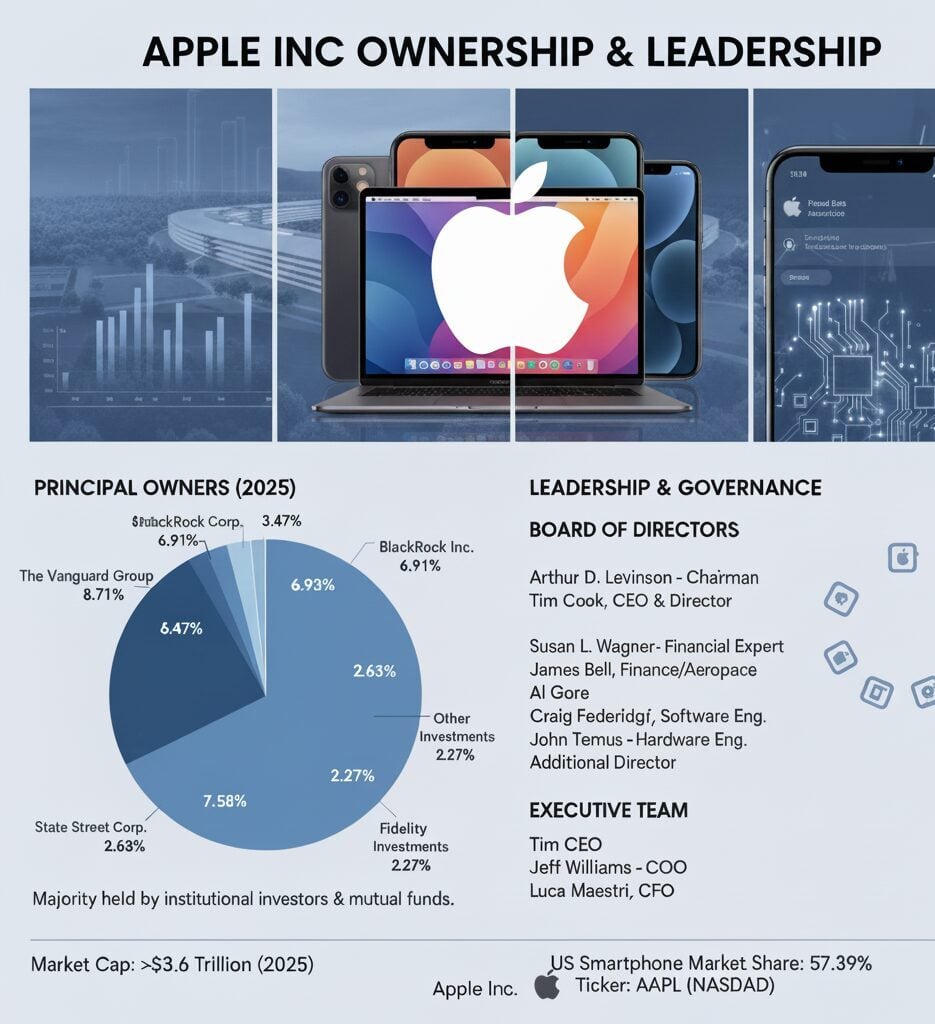

Apple Inc. remains one of the world’s most valuable technology companies, with ownership primarily distributed among institutional investors and mutual funds. The Vanguard Group leads as the largest shareholder with 8.71% ownership, followed by BlackRock at 6.91%.
As of 2025, Apple maintains its position as a technology giant with a market capitalization exceeding $3.6 trillion. The company continues to dominate the smartphone market with a 57.39% share in the United States and approximately 20% globally. Under Tim Cook’s leadership since 2011, Apple has expanded its ecosystem beyond hardware into services, generating $96.2 billion from its services division alone in fiscal year 2024.
Who owns Apple?
Apple’s ownership structure consists primarily of institutional investors who collectively hold the majority of shares. No single entity controls Apple outright, as the company operates as a publicly traded corporation on the NASDAQ exchange under the ticker symbol AAPL.
The top ten institutional shareholders control approximately 31.57% of Apple’s outstanding shares. These investment firms manage retirement funds, index funds, and mutual funds, meaning millions of individual investors indirectly own portions of Apple through these vehicles.
Ownership Distribution
Institutional investors dominate Apple’s shareholder base, with investment management companies holding the largest stakes. The remaining shares are distributed among individual retail investors, Apple employees with stock options, and company executives who receive equity compensation as part of their packages.
Largest shareholders of Apple
Apple’s shareholder landscape features some of the world’s most influential investment firms. These institutional giants manage trillions in assets and view Apple as a cornerstone holding in their portfolios.
The Vanguard Group – Leading Shareholder
The Vanguard Group maintains the largest position in Apple with 1.32 billion shares, representing 8.71% ownership. As one of the world’s largest asset managers with over $7 trillion under management, Vanguard’s substantial stake reflects strong confidence in Apple’s long-term prospects. The firm holds Apple shares across numerous index funds and actively managed portfolios.
BlackRock Inc. – Second Largest Holder
BlackRock controls approximately 1.05 billion Apple shares, equating to 6.91% ownership. The investment giant, managing over $10 trillion globally, includes Apple as a core holding in its iShares ETFs and institutional portfolios. BlackRock’s position gives it significant voting power in corporate decisions.
State Street and Berkshire Hathaway
State Street Corporation owns 528.08 million shares (3.47%), while Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway holds 400 million shares (2.63%). Buffett famously called Apple “probably the best business I know in the world” and has maintained Berkshire’s position as one of its largest equity investments [1].
Additional Major Investors
Fidelity Investments owns 345.64 million shares (2.27%), followed by Geode Capital Management with 313.37 million shares (2.06%). Morgan Stanley, T. Rowe Price, JPMorgan Chase, and Norway’s sovereign wealth fund (Norges Bank) round out the top ten shareholders, each controlling between 1-2% of outstanding shares.
History of Apple Co-founders
Apple Computer Company originated in Los Altos, California, on April 1, 1976, when Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne launched their venture from Jobs’ family garage. The trio aimed to democratize computing technology, making it accessible beyond large corporations and institutions.
The Founding Team
Steve Wozniak engineered the Apple I computer as a bare circuit board, while Jobs envisioned its commercial potential. Ronald Wayne, who owned 10% of the company, sold his stake for $800 just twelve days after incorporation, a decision worth over $300 billion today. Microsoft, Apple’s future rival, would be founded just one year later in 1975.
Early Growth and Public Offering
The Apple II, launched in 1977, became one of the first mass-produced personal computers with color graphics and an open architecture. By December 12, 1980, Apple went public at $22 per share, raising $101 million and creating more millionaires than any IPO since Ford Motor Company.
Jobs’ departure in 1985 following boardroom disputes led to a difficult period. His return in 1997 after Apple acquired NeXT marked the beginning of an unprecedented transformation, introducing revolutionary products like the iMac, iPod, and eventually the iPhone in 2007.
Who is on the board of directors for Apple?
Apple’s board of directors comprises eight members who oversee corporate governance and strategic direction. The board ensures management acts in shareholders’ best interests while maintaining Apple’s innovative edge.
Leadership and Technology Expertise
Arthur D. Levinson
Former Genentech CEO bringing biotechnology expertise and strategic vision to Apple’s board leadership.
Tim Cook
Leading Apple since 2011, overseeing the company’s expansion to a $3.6 trillion valuation.
Craig Federighi and John Ternus represent Apple’s technical leadership on the board. Federighi oversees software engineering including iOS and macOS development, while Ternus leads hardware engineering for iPhone, iPad, and Mac product lines.
Financial and Investment Background
Susan L. Wagner, co-founder of BlackRock, provides crucial financial markets insight. Her experience building one of the world’s largest asset managers helps guide Apple’s capital allocation strategies. James Bell, former Boeing CFO, contributes aerospace industry experience and financial management expertise.
The board’s compensation structure aligns with shareholder interests through equity grants. Directors receive annual retainers of approximately $300,000 plus restricted stock units valued at $300,000, ensuring their interests align with Apple’s long-term success [2].
Sustainability and Public Policy
Al Gore, former U.S. Vice President, joined Apple’s board in 2003, contributing environmental sustainability expertise. His influence helped shape Apple’s commitment to carbon neutrality and renewable energy initiatives. The company achieved carbon neutrality for corporate operations in 2020.
The board meets at least four times annually, with additional special meetings as needed. Committees include Audit and Finance, Compensation, and Nominating and Corporate Governance, each addressing specific oversight responsibilities.
Executive Management Team
Beyond board members, Apple’s executive team drives operational excellence. Jeff Williams serves as Chief Operating Officer, managing the complex supply chain spanning multiple continents. Luca Maestri, CFO since 2014, oversees financial planning and maintains investor relations.
The executive compensation structure emphasizes performance-based rewards. Tim Cook’s 2024 compensation totaled $63 million, with the majority tied to stock performance and operational metrics. This structure ensures leadership focuses on long-term value creation rather than short-term gains.
FAQs
▸ Who is Apple’s largest shareholder?
The Vanguard Group owns the most Apple shares with 8.71% ownership (1.32 billion shares), followed by BlackRock at 6.91%.
▸ Does Tim Cook own Apple?
No, Tim Cook serves as CEO but doesn’t own Apple. He holds shares through compensation but institutional investors own the majority.
▸ How much of Apple does Warren Buffett own?
Berkshire Hathaway owns approximately 2.63% of Apple (400 million shares), making it one of Buffett’s largest investments.
▸ What companies has Apple acquired?
Apple owns Beats Electronics, Shazam, Dark Sky, PrimeSense, AuthenTec, and dozens of other technology companies acquired since 1988.
▸ Who makes decisions at Apple?
Apple’s Board of Directors and executive team led by CEO Tim Cook make strategic decisions, with shareholder input during annual meetings.
